Sicilia
Sicily is located across the toe of Italy’s boot. It is separated by the mainland of Italy by the Strait of Messina. This narrow strait is between Sicily and Calabria and its narrowest point is only 3km (2 miles) wide. Sicily is the largest island of Italy and the Mediterranean. Sicily is rich in history, traditions, art, and culture.
Thanks to its magnificent coast and beaches, Sicily is a very popular tourist destination. It has coasts on 3 different seas: the Mediterranean to the south, the Tyrrhenian Sea to the north and the Ionian to the east. It has more than 200 beaches. Some of the most dramatic beaches are on the tiny Aeolian Islands, to the north of Sicily. There you’ll find midnight-black beaches, a legacy of volcanic activity, and rust red sand dunes. Lapari, one of the islands, has the largest beach made of pumice stone.
The tallest active volcano in Europe is located in Sicily. Mount Etna is located on the eastern coast of the island and its 3,326 meters high.
Capital – Palermo
Palermo is located on Sicily’s northwestern coast at the head of the Bay of Palermo. Palermo is Sicily’s chief port and center of government. The port operates both merchant and passenger lines to Tunisia and Naples and handles most of the island’s foreign trade.
Citrus fruits, cereals, fresh fish, and chemicals are among Palermo’s principal exports. Ship repair is an important industry, as is the manufacture of chemicals, glass, cement, machinery, and processed foods. Sicily is the 4th biggest wine producer in Italy and is famous for the production of Marsala wines. Palermo is Sicily’s chief port and center of government.
Foods of Lazio

Arancini
Rice balls filled with meat sauce, peas, dried prosciutto, mozzarella and pecorino, tomatoes and sometimes dried capers.

Pasta alla Norma
Pasta with eggplants, ricotta cheese and fresh basil.

Cannoli
Crispy fried pastry tubes filled with ricotta cheese cream – one of Sicily’s best dessert.

Granita
A semi-frozen dessert made with water, sugar and various flavours. It is tradition to add coffee to it.

Cassata
The most famous Sicilia dessert. A traditional sponge cake layered with ricotta, fruit preserves and drenched in genoise liquor. This beautiful dessert is then decorated with a marzipan shell and candied fruits.

Scaccia
Long rectangular stuffed flatbread consisting of various combinations of ingredients such as ricotta cheese and onion, cheese and tomato, tomato and onion, or tomato and eggplant.

Pasta chi Sardi
Pasta with saffron, sardines, wild fennel, pine nuts and raisins.
UNESCO World Heritage Sites in Sicilia
Archaeological Area of Agrigento
Agrigento
A Greek colony founded in the 6th century BCE, developed into one of the major cities of Magna Graecia and of the Mediterranean. Several Doric temples have been preserved, and they represent one of the most notable sites of Greek art and culture.

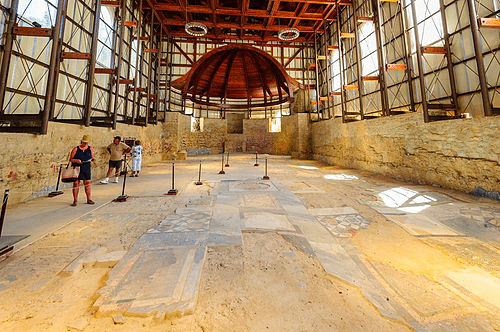
Villa Romana del Casale
Enna
The villa in Piazza Armerina is one of the most luxurious Roman villas built in the early 4th century, and is a representative example of the economy and social structure of its period. It is richly decorated with mosaics of exceptional quality.
Isole Eolie (Aeolian Islands)
Messina
This archipelago off the coast of Sicily has been extensively studied by geologists since at least the 18th century. The islands contain several classical features of volcanic landforms, which were important in the development of volcanology as a scientific discipline. Two types of volcanic eruptions bear names after the islands of the archipelago; Strombolian and Vulcanian.


Late Baroque Towns of the Val di Noto
Catania, Ragusa, Syracuse
In 1693, a powerful earthquake hit Sicily, destroying several towns and cities. In the aftermath, the towns of Caltagirone,Militello Val di Catania, Catania, Modica, Noto, Palazzo lo, Ragusa, and Scicli were rebuilt in line with the Baroque urban planning trends. They represent the pinnacle of late Baroque art in Europe.
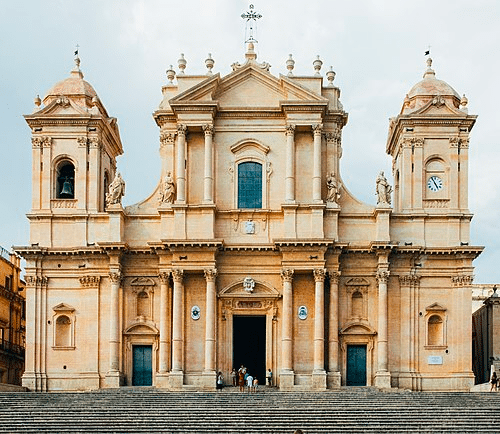
Syracuse and the Rocky Necropolis of Pantalica
Syracuse
Syracuse was founded in the 8th century BCE by the Corinthians and became one of the most important cities of Magna Graecia. An important monument from this period is the Doric Temple of Apollo. The Necropolis of Pantalica (pictured) contains more than 5,000 tombs, most dating from the 13th to the 7th centuries BCE, and remains of Byzantine era structures.


Mount Etna
Catania
Mount Etna is the most active stratovolcano in the world, as well as one of the most studied volcanoes, with at least 2,700 years of documented history. It features several typical volcanic phenomena, such as cinder cones, lava flows, and lava caves. The mountain also supports a particular ecosystem with endemic flora and fauna.
Arab-Norman Palermo and the Cathedral Churches of Cefalù and Monreale
Metropolitan City of Palermo

